Divergence Trading System
November 22, 2019
Oscillators are powerful trading indicators offered by any Forex broker. Almost all of them show overbought and oversold conditions and traders try to get as early in a trade as possible.
However, the problem with buying oversold and selling overbought markets is that this Forex trading system works only when the market is in a range. When it trends, it tends to stay far too long in oversold or overbought conditions, making it difficult for traders to find the right positioning.
Divergences help to spot trend reversals. A divergence forms when the price of a currency pair and oscillator begin moving in opposite directions.
Traders use oscillators to compare the price of a currency pair with the one of the oscillator. In normal conditions, they both show the same thing: if the price makes a new high, the oscillator should confirm that too, creating a new high as well. Or, if the price makes a new lower low, the oscillator should establish that lower low also.
When the oscillator doesn’t do that, it means that the price and the oscillator formed a divergence. Because the oscillator always considers more periods to plot its values, traders stick with what the oscillator shows, and now what the actual price indicates.
Therefore, trading the Forex market with a system based on divergences means comparing the price action of a currency pair with the oscillator.
How to Trade Divergences with an Oscillator
Divergences are a great tool to use in technical analysis. They show a possible market reversal and traders trust them most then the actual price. For a good reason, we might say, as oscillators consider multiple periods before plotting a value corresponding to the current price candlestick.
Here’s how divergences work in Forex analysis. First, they are of two types: bullish and bearish divergences. As the name suggests, a bullish divergence forms at the bottom of a bearish trend, indicating buying conditions are in place.
On the other hand, a bearish divergence appears right at the top of a bullish trend, showing selling conditions.
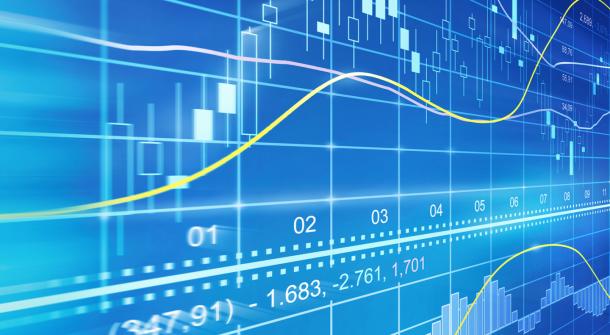
The AUDUSD chart from above is self-explanatory. It is a “naked” chart (i.e., it doesn’t have any technical analysis tools common in Forex trading, but only an oscillator: the RSI or Relative Strength Index showing the default periods: 14.
Effectively, it means that the RSI considers the previous fourteen candlesticks before plotting the actual value corresponding to the current price. For this reason, traders “trust” more what the oscillator shows, rather than what the price tells.
A Forex strategy based on divergences considers bullish and bearish differences between the price and the oscillator’s moves. The bullish divergence from the chart above shows exactly that: while the price made two consecutive lower lows, the RSI failed to confirm the second lower low. Traders that use such a system will trust what the RSI show and buy the AUDUSD on the grounds of a bullish divergence that just formed.
Conclusion
Divergences do not work all the time. They are a great way to find possible market reversals, but sometimes the market remains in a divergence more than the trader can remain solvent. To overcome this, traders use a stop-loss right at the bottom of the RSI in a bullish divergence setup.